Table of Contents
Factoring finance in India
Factoring is one of the upcoming sources of finance for SMEs in India. It is particularly, relevant if a company is growing daily and when new customers are added regularly; there are chances of ending up with huge invoices. This problem often directs many businesses to look for an alternative source of finance like factoring.
What is factoring?
Factoring is a financial option for the management of receivables. In a simple definition, it is the conversion of credit sales into cash. In factoring, a financial institution (factor) buys the accounts receivable of a company (Client) and pays up to 80% (rarely up to 90%) of the amount immediately on agreement. The factoring company pays the remaining amount (Balance 20% minus finance cost minus operating cost) to the client when the customer pays the debt. Collection of debt from the customer is done either by the factor or the client depending upon the type of factoring.
The account receivable in factoring can either be for a product or service. Examples are factoring against goods purchased, factoring in construction services (in government contracts it is assured that the government body can pay back the debt in the stipulated period of factoring, and hence contractors can submit the invoices to get cash instantly), factoring against medical insurance, etc. Let us see how factoring is done against an invoice of goods purchased.
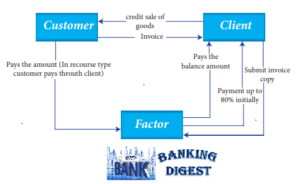
The different types of Factoring
a) Recourse and Non-recourse Factoring:
In this type of arrangement, the financial institution can resort to the firm, when the debts are not recoverable. So, the credit risk associated with the trade debts is not assumed by the factor.
On the other hand, in non-recourse factoring, the factor cannot recourse to the firm, in case the debt turn out to be irrecoverable.
b) Disclosed and Undisclosed Factoring:
The factoring in which the factor’s name is indicated in the invoice by the supplier of the goods or services asking the purchaser to pay the factor, is called disclosed factoring.
Conversely, the form of factoring in which the name of the factor is not mentioned in the invoice issued by the manufacturer. In such a case, the factor maintains the sales ledger of the client, and the debt is realized in the name of the firm. However, the control is in the hands of the factor.
c) Domestic and Export Factoring:
When the three parties to factoring, i.e. customer, client, and factor, reside in the same country, then this is called domestic factoring.
Export factoring, otherwise known as cross-border factoring is one in which there are four parties involved, i.e. exporter (client), the importer (customer), the export factor, and the import factor. This is also termed the two-factor system.
d) Advance and Maturity Factoring:
In advance factoring, the factor gives an advance to the client, against the uncollected receivables.
In maturity factoring, the factoring agency does not provide any advance to the firm. Instead, the bank collects the sum from the customer and pays to the firm, either on the date on which the amount is collected from the customers or on a guaranteed payment date.
Advantage of Factoring
The advantage of the factoring options are as follows:
- It helps to improve the current ratio. Improvement in the current ratio is an indication of improved liquidity. Enables better working capital management. This will enable the unit to offer better credit terms to its customers and increase orders.
- It is an increase in the turnover of stocks. The turnover of stock into cash is sped up and this results in a larger turnover on the same investment.
- It ensures prompt payment and reduction in debt.
- It helps to reduce the risk. Present risk in bill financing like finance against accommodation bills can be reduced to a minimum.
- It is helpful to avoid the collection department. The client need not undertake any responsibility of collecting the dues from the buyers of the goods.
Limitations of Factoring
The factoring option has some limitations, which are as follows:
- Factoring is a high-risk area, and it may result in over-dependence on factoring, mismanagement, over-trading, or even dishonesty on behalf of the clients.
- It is uneconomical for small companies with less turnover.
- The factoring is not suitable for the company’s manufacturing and selling highly specialized items because the factor may not have sufficient expertise to assess the credit risk.
- The developing countries such as India are not able to be well versed in factoring. The reason is lack of professionalism, non-acceptance of change, and developed expertise.

Thanks for sharing this information
Thank you for your feedback.